
#Barrier pitfall trap how to
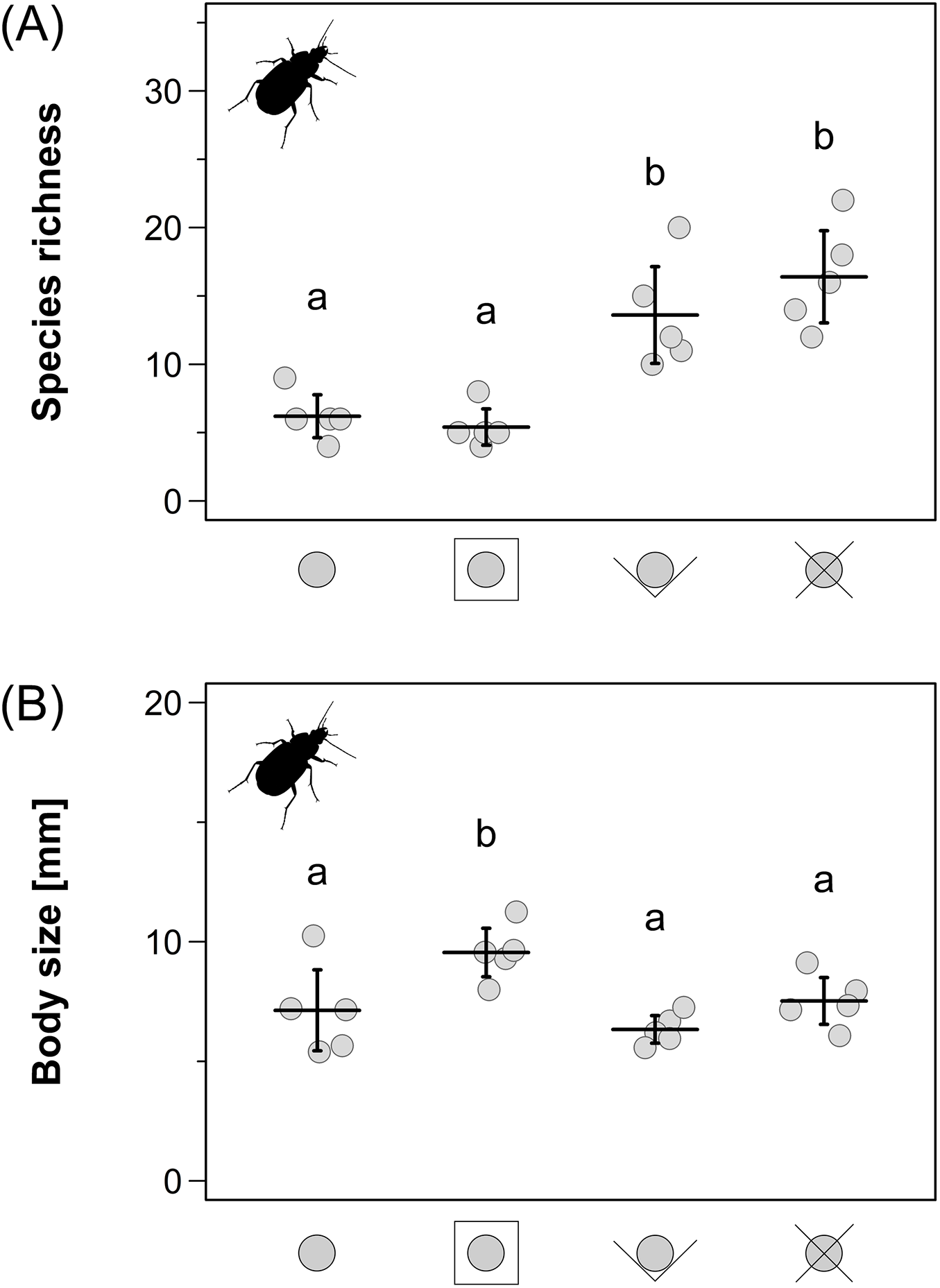
Chapter IV: How to record predation rates? A plethora of methods has been proposed and used for recording predation rates, but these have rarely been validated before use. Placing several simple pitfall traps in the field can compensate the difference while still saving handling effort. While barrier traps collected more species and deliver more complete species inventories, conventional simple pitfall traps provide reliable results with comparatively little handling effort. I compared different types of pitfall traps that had been used in previous studies in respect to resulting carabid beetle assemblages. Pitfall traps are widely used to record ground dwelling predators, but little is known about how different trap types affect catches. Chapter III: How to record ground dwelling predators? Testing methodology is critical as it ensures scientific standards and trustworthy results. Moreover, I validated the methodology I used to assess predator assemblages and predation rates (Chapters III & IV).

I recorded biodiversity and pest control potentials using a variety of different methods (Chapters II, V, VI & VII). Here I investigated how effective different AES habitats are for restoring biodiversity in different agricultural landscapes (Chapter V) and whether they benefit natural pest control in adjacent oilseed rape (Chapter VI) and winter cereal fields (Chapter VII).
However, little is known about how well different AES habitats fulfil this purpose and whether they benefit ecosystem services in adjacent crop fields. These AES combine special management regimes with the establishment of tailored habitats to create refuges for biodiversity in agricultural landscapes and thus ensure biodiversity mediated ecosystem services such as pest control. To counter this ‘biodiversity crisis’, agri-environment schemes (AES) have been introduced as part of ecological intensification efforts. Chapters I & II: General Introduction & General Methods Agriculture is confronted with a rampant loss of biodiversity potentially eroding ecosystem service potentials and adding up to other stressors like climate change or the consequences of land-use change and intensive management.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
